To get the mouse position relative to an element, first get the X and Y coordinates of the mouse pointer using the clientX and clientY properties and then subtract the left and right offsets of the element from these coordinates.
The clientX and clientY properties are the properties of the MouseEvent object.
The clientX property returns the X coordinate of the mouse pointer, while the clientY property returns the Y coordinate of the mouse pointer relative to the viewport.
Therefore, if you want to get the mouse position relative to the element, you have to subtract the left and right offsets of the element from the value of the clientX and clientY respectively.
Let’s say we have a div element in our HTML document and we want to get the mouse position relative to this div as we move the mouse:
<div id="box">
Mouse Pos: <b><span id="mousePos"></span></b>
</div>
Add some CSS:
div{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
border: 2px solid grey;
margin-left: 100px;
margin-top: 50px;
padding: 10px;
}
Add the JavaScript:
// Get references to the elements
const elem = document.getElementById('box');
const mousePos = document.getElementById('mousePos');
// Attach mousemove event
elem.addEventListener('mousemove', function(event){
// Get the target
const target = event.target;
// Get the bounding client
const rect = target.getBoundingClientRect();
// Get X & Y coordinates
let xPos = event.clientX - rect.left;
let yPos = event.clientY - rect.top;
// Print the XY-coordinates
mousePos.innerText = `(${xPos}, ${yPos})`;
});
Output:

In the above code, we have used the getBoundingClientRect() method to get the left and top offsets of the element.
The getBoundingClientRect() method returns a DOMRect object. This object contains the x, y, top, left, bottom, right, width and height properties of the element.
Note that each value is in the pixels unit.
const elem = document.getElementById('box');
console.log(elem.getBoundingClientRect());
Output:
{
"x": 108,
"y": 50,
"width": 224,
"height": 224,
"top": 50,
"right": 332,
"bottom": 274,
"left": 108
}
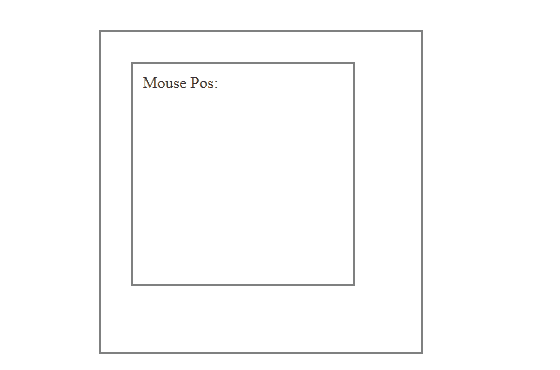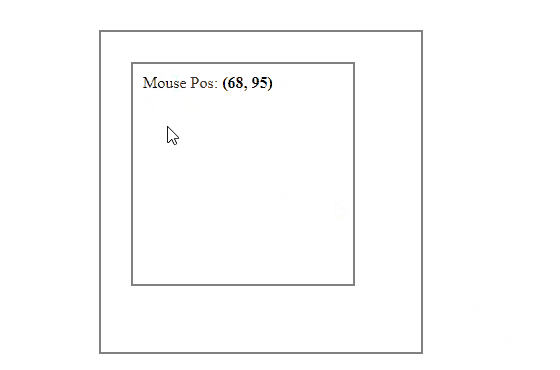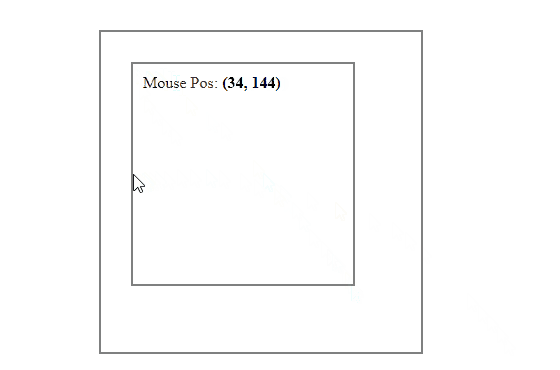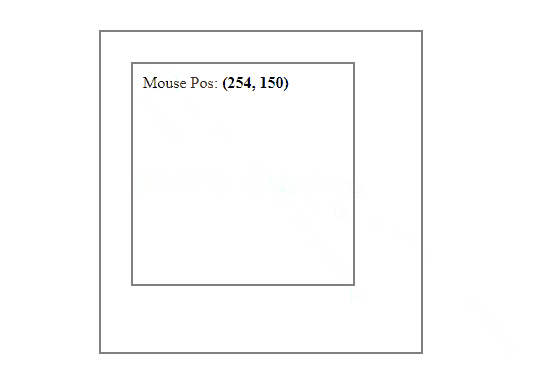
Get the Mouse Position Relative to the Parent Element with JavaScript
Getting the mouse position relative to the parent is almost similar to getting the mouse position relative to the element itself.
To get the mouse position relative to the parent element, first get the X and Y coordinates of the mouse using the clientX and clientY properties and then subtract the left and top offsets of the parent instead of the element from these coordinates.
For example, let’s say we have a div element inside another div and we want to get the mouse position inside the inner div but relative to its parent:
<div id="parent">
<div id="box">
Mouse Pos: <b><span id="mousePos"></span></b>
</div>
</div>
Add some CSS:
#parent{
width: 300px;
height: 300px;
border: 2px solid grey;
margin-left: 100px;
margin-top: 50px;
padding: 10px;
}
#box{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
border: 2px solid grey;
padding: 10px;
margin-left: 20px;
margin-top: 20px;
}
Add the JavaScript:
// Get references to the elements
const elem = document.getElementById('box');
const parent = document.getElementById('parent');
const mousePos = document.getElementById('mousePos');
// Attach mousemove event
elem.addEventListener('mousemove', function(event){
// Get the target
const target = event.target;
// Get the parent's bounding client
const parentRect = parent.getBoundingClientRect();
// Get X & Y coordinates
let xPos = event.clientX - parentRect.left;
let yPos = event.clientY - parentRect.top;
// Print the XY-coordinates
mousePos.innerText = `(${xPos}, ${yPos})`;
});
Output:
Thanks for reading.

